| Monthly Tech-Tip | No tracking! No ads! |
G2926B cone 6 transparent liner glaze: Proven, reliable, durable
While colorful and layered glazes on the outsides of pieces get lots of praise and glory, transparent or white glazes providing the functional surface on the insides of pieces often get little attention from potters. Really, what good is an attractive piece if the food surface is crazing, blistering, leaching or cutlery marking? Or if it converts the piece into a time bomb? This cone 6 liner glaze, G2926B, is an example of how I found a glaze, recognized its potential and then adjusted the recipe to resist crazing on our clay bodies, fire durable and leach resistant and act as a base to host colorants, opacifiers and variegators. I get the best fired results using the C6DHSC firing schedule and very good performance as a dipping glaze when the slurry is thixotropic. One of the reasons this recipe is so widely used is that it is well-documented, having a code number that Google indexes. Drinking from a mug having a quality and fitted functional surface and a nice crisp line dividing the outside and inside glazes instills pride in me as the maker. What is the outside glaze? It is the G2934Y matte base recipe plus 8% Mason 6027 stain. The clay is MNP which I make myself.
Related Pictures
Meet two glazes at the rim using wax emulsion. Why? How?

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
Reactive glazes (melt-mobile, crystallizing or heavily pigmented) are the least suitable for food surfaces because they have the potential to leach metals. Liner glazing ware is an excellent way to deal with this problem. Not only does this approach improve functionality but it can be aesthetically pleasing and practical in production.
This liner is GA6-B, a pottery glaze recipe we promote with confidence. Not only is it less likely to be leaching metals but also less likely to craze - this assures water tightness on non-vitreous bodies and eliminates any potential for bacteria growth in the cracks (especially if the body has porosity). Unfortunately, glazes that leach are also likely to stain and cutlery mark - these add more reasons why they are most often unsuitable for food surfaces.
The straightness of the dividing line is affected by both the application technique and the degree to which the two glazes bleed into each other and run. Read and watch our liner glazing step-by-step and liner glazing video for details on how to do this - it is practical for any potter or hobbyist (or even in production). And tap/click the picture above for other examples of this.
Mason stains in the G2926B base glaze at cone 6
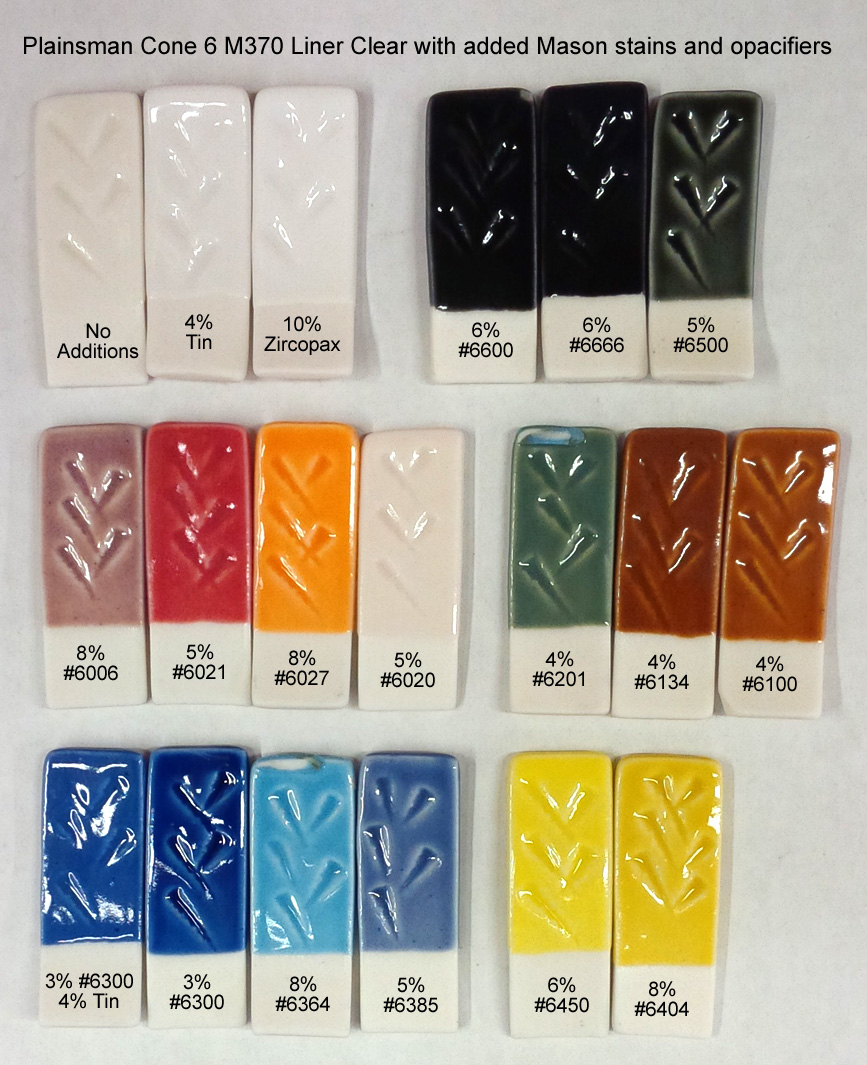

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
This glaze, G2926B, is our main glossy base recipe. Stains are a much better choice for coloring it than raw metal oxides. Other than the great colors they produce here, there are a number of things worth noticing. Stains are potent; the percentages needed are normally much less than for metal oxides. Staining a transparent glaze produces a transparent color, it is more intense where the laydown is thicker - this is often desirable in highlighting contours and designs. For pastel shades, add an opacifier (e.g. 5-10% Zircopax, more stain might be needed to maintain the color intensity). The chrome-tin maroon 6006 does not develop well in this base (alternatives are G2916F or G1214M). The 6020 manganese alumina pink is also not developing here (it is a body stain). Caution is required with inclusion stains (like #6021). Bubbling, as is happening here, is common - this can be mitigated by adding 1-2% Zircopax. And it’s easy to turn any of these into brushing or dipping glazes.
G2934 cone 6 DIY MgO matte glaze: Reliable, durable, adjustable, stainable

This picture has its own page with more detail, click here to see it.
These pieces were made from Plainsman Polar Ice and fired to cone 6 using variations on the PLC6DS and C6DHSC schedules. The dipping glaze is G2934Y, a recipe variant of G2934 having a finer micro-surface texture (it has the same chemistry but the MgO is sourced from a frit and talc instead of dolomite). These mugs display how well the recipe works with stains and the varying degrees of matteness we can achieve by varying the cooling rate and the percentage of glossy G2926B base blended in. As an MgO matte, this glaze can have a surface pleasant to the touch. It fires durable, can be quite matte without cutlery marking and it has very good slurry and application properties (as a dipping glaze). It has a very low thermal expansion (won’t craze). It works really well with stains (except purples). It melts even better than the glossy!
Videos
 |
How I Developed the G2926B Cone 6 Transparent Base Glaze
How I found a pottery glaze recipe on Facebook, substituted a frit for the Gerstley Borate (using glaze chemistry), compared using a melt flow tester, added as much extra SiO2 as it would tolerate, and got a durable and easy-to-use cone 6 clear. |
Links
| URLs |
https://insight-live.com/insight/share.php?z=Zq1w2TE6SL
The Development of G2926B Cone 6 Clear Glaze |
| Recipes |
G2926B - Cone 6 Whiteware/Porcelain transparent glaze
A base transparent glaze recipe created by Tony Hansen, it fires high gloss and ultra clear with low melt mobility. |
| Glossary |
Transparent Glazes
Every glossy ceramic glaze is actually a base transparent with added opacifiers and colorants. So understand how to make a good transparent, then build other glazes on it. |
| Glossary |
Medium Temperature
These are stoneware glazes that fire in the range of 1200C (2200F). They often contain boron to assist with melting. |
Got a Question?
Buy me a coffee and we can talk

https://backup.digitalfire.com, All Rights Reserved
Privacy Policy

